- Home
- EXO2 Water Quality Sonde Rental
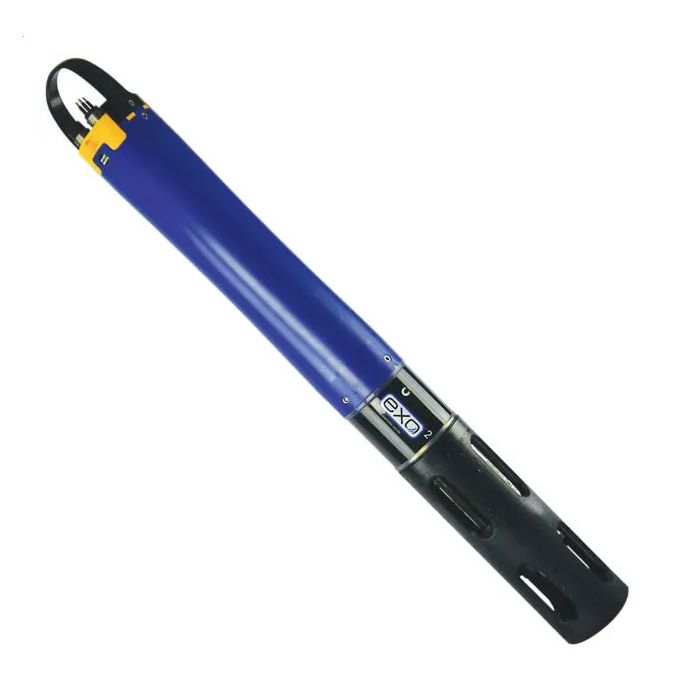
EXO2 Water Quality Sonde Rental
Features
- 2 spare ports for adding Total Algae and/or fDOM sensors
- Internal battery pack for unattended logging
- Central wiper prevents fouling and extends deployment
This item is currently on order from the manufacturer, but it has not yet arrived to our warehouse.
For a current estimate of availability, please call 888-426-2151 or or fill out the form below:
This item drop ships directly from the manufacturer, and the actual lead time is dependent on availability at their warehouse.
For a current estimate of availability, please call 888-426-2151 or or fill out the form below:
Fulfillment times may be longer than usual due to component shortages and other factors outside of our control.
For a current estimate of availability, please call 888-426-2151 or or fill out the form below:
Shipping, Delivery, Order Processing & Product Availability
Fondriest uses the best carriers to make sure orders gets to you on time. Learn more about shipping times, methods, costs, and carriers.
Delivery Time
We keep you informed. Shortly after you place your order, you will receive an Order Acknowledgement email to confirm your order details, including shipping and a delivery estimate. Once your order has been prepared for shipment and ships, you will receive a Shipment Notification email with carrier and tracking information.
Shipping and Delivery Estimates
The 'Ships' timeframe is an estimate of when the item will ship from our warehouse. All items will ship at one time unless you specifically request partial shipment. In which case, the items on your order will ship as they become available. The 'Delivers' timeframe is an estimate of when the item will be delivered to your shipping address after it ships. The estimated delivery time depends on the shipping method you choose during checkout. All estimates are based on business days.
Shipping Options
Fondriest offers several convenient shipping options via UPS.
| Ground Shipping: | Products shipped via ground service are normally delivered within five business days after shipment. |
| 2-Day Shipping: | For an additional charge, Fondriest offers 2-day shipping for most products. Products shipped via two-day service prior to 4:00 p.m. EST are normally delivered by 7:00 p.m. local time two business days after shipment. |
| Overnight Delivery: | For an additional charge, Fondriest offers overnight shipping for most products. Products shipped via overnight service prior to 4:00 p.m. EST are normally delivered by 7:00 p.m. local time one business day after shipment. Earlier overnight delivery options may also be available depending on the destination. |
| Your Account: | For no additional charge, Fondriest can ship on third-party customer accounts via UPS and FedEx. Note that FedEx Ground shipments are picked up the following business day and Express shipments must be made before 1:00 p.m. EST to ensure same-day pick-up. |
Remember that these estimates are for time in transit only, and that they do not apply until the product leaves the Fondriest warehouse. As the delivery of your order is beyond Fondriest's control once your order leaves the Fondriest warehouse, we cannot assume liability for late deliveries, regardless of the delivery method you specify.
Signature Required on Most Deliveries
Most of Fondriest's shipments contain valuable equipment. If you will not be at the shipping address to accept delivery of your product, consider shipping the item to an address where someone you trust will be available to sign for your package, or accept your package if a signature is not required for the delivery. Once your order has prepared for shipment or has shipped, we are unable to change the shipping address. Title and risk of loss to all products will pass to you on delivery. If you are willing to assume the risks of delivering your order without a signature, you may authorize Fondriest to arrange for a delivery that does not require anyone to be at the delivery address.
Undeliverable Packages
Occasionally packages are returned to Fondriest as undeliverable. When the carrier returns an undeliverable package to Fondriest, please contact us to make arrangements for reshipment.
Failed Delivery Attempts
Most of Fondriest carriers make three attempts to deliver a package. After three delivery attempts, the carrier will return the package to Fondriest.
Order Processing
The estimated shipment date on your order is based on product availability, payment processing time, and warehouse processing time and does not include transit time. We do not begin payment processing until Fondriest receives all of the information that is needed and full payment or a full authorization, in the case of credit card or rental orders.
Fondriest will begin payment processing for orders placed on weekends or holidays on the next business day. Business days are Monday through Friday, excluding federal holidays.
Your order for in-stock items that are eligible for same-day shipping must be received before your local time of 2:00 p.m., pending payment processing, for there to be adequate remaining time in the day for your order to be dispatched.
Product Availability
Fondriest makes every effort to ship your product according to the estimated lead times. The estimated lead times are in business days (Monday through Friday, excluding federal holidays).
Although Fondriest makes every effort to ship your order according to the lead time provided, shipping dates may change due to changes in supply. If the lead time changes, Fondriest will contact you via email and provide a revised shipping estimate.
Fondriest makes every effort to supply the products you order, but there may be occasions when Fondriest confirms orders and later learns that it cannot supply the products, either at all or in the quantities ordered. Although rare, these occasions can include when Fondriest learns that the products no longer are being manufactured or they otherwise become unavailable, when Fondriest cannot source components for the configuration you ordered, or when there was a pricing error at the Fondriest Online Store.
In those circumstances, Fondriest will inform you and, if you are interested, Fondriest may suggest alternative products that may meet your needs. If you do not wish to order alternative products, Fondriest will cancel your order for products that cannot be supplied and for any other products that you no longer wish to order as a result, and will refund your purchase price.
We want you to be completely satisfied with your purchase. If you are not, you may initiate a return within 30 calendar days of receiving your item(s). To begin a return, you must request a Return Material Authorization (RMA) by either contacting your account representative or the general customer support address: customercare@fondriest.com. Returns without an RMA will not be accepted.
Items returned for credit must be new, unused, and in the original packaging (including any accessories, manuals, and documentation that shipped with the product). Returned items must be received by Fondriest Environmental within 14 calendar days of the issuance of the RMA. All returned items are subject to inspection and approval prior to the issuance of any credit. If the returned items have been approved, Fondriest will issue a credit based on the original method of payment. Please note that items may be subject to a manufacturer's restocking fee.
Non-Returnable Items: Fondriest does not permit the return of or offer refunds for the following products:
- Configured-to-order or customized products
- Hazardous materials
- Opened calibration reagents
- Opened software
- Software downloads
- Fondriest Gift Cards
Fondriest recommends using a carrier that offers shipment tracking for all returns. Packages should be insured for the full value in case of loss or damage. Fondriest does not assume any liability for loss or damage to the product during shipping.
- Free ground shipping
- Expedited repair and warranty service
- Lifetime technical support
- More
At Fondriest, we are committed to providing high-quality products at affordable prices with the industry's best support. Additionally, we offer:
-
Discounts
High volume purchases lead to favorable pricing, which is passed on to the customer by way of discount off MSRP.
-
Assembly, Test and Calibration
Sensors and instruments are assembled, tested and calibrated prior to shipment. A calibration report is included.
-
Lifetime Technical Support
A knowledgeable staff of applications engineers provides ongoing support for the life of the product.
-
Product Training
Applications engineers are available for webinars or personalized, on-site startup and training. Extensive measurement technology, product troubleshooting and instrument repair workshops are offered at the Field Station.
-
Extended Warranties
Warranties extended beyond factory standards are offered on many items to ensure a lasting useful life.
-
Repair
A factory-authorized service center provides fast turnaround product repair and annual maintenance.
-
Rental
Rental equipment is available to minimize downtime and cover equipment needs when projects expand.
-
Communications
Call, email or chat online with applications engineers. Email correspondence is responsive and a toll-free number is available for added convenience.
-
Quick Ship
Many orders ship on the same day and expedited shipping is available. If a product cannot be shipped immediately, customers are notified by phone or email.
-
Discounts
Simultaneously measure and log temperature, conductivity, salinity, TDS, resistivity, dissolved oxygen (optical), pH, ORP, and turbidity with a central wiper to extend the deployment and reduce maintenance.
- (1) EXO2 sonde with integrated depth sensor
- (1) Temperature/conductivity sensor
- (1) pH/ORP sensor
- (1) Optical dissolved oxygen sensor
- (1) Optical turbidity sensor
- (1) Central wiper
- (1) USB adapter
- (1) Soft-sided carrying case
- (1) USB drive with KOR software
- (1) Calibration cup
- (1) Probe guard
- (4) D-cell alkaline batteries
- (1) Maintenance kit
- (1) Calibration report
Select Options








have been added to your cart
There are items in your cart.
Cart Subtotal: $xxx.xx
We can't add this item to your shopping cart right now. Please reload the page.
Please first select the items and quantities to add to your Cart.
In The News
Measuring Harmful Algal Bloom Toxins Using Real-Time Data Buoys in the Great Lakes
While harmful algal blooms (HABs) are a significant issue in the Great Lakes that have been monitored using real-time data buoys, there is still no automated method for measuring the toxins produced by these blooms. Todd Miller, an affiliate and associate professor at the University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee and principal investor at the Laboratory for Aquatic Microbiology and Chemistry , is currently working toward a solution that allows for the prediction of toxin concentrations through the use of real-time lake data. The toxins produced by HABs—microcystins, cylindrospermopsin, and anatoxins—can be exposed to humans and animals through a variety of methods.
Real-Time Monitoring in Rhode Island: Narragansett Bay Fixed Station Monitoring Network
Narragansett Bay in Rhode Island has a long history of water quality issues resulting from land pollution, leading to the influx of nutrients into the bay, which can cause algal blooms and declines in dissolved oxygen. The resulting hypoxia and thermal stratification are of particular concern due to their impacts on the coastal fishery. “To understand these shifts throughout Narragansett Bay, a small group of researchers were established in 1999 to monitor physical water quality parameters on a continuous basis,” explains Heather Stoffel, a marine research associate at the University of Rhode Island ( URI ) and Quality Assurance Officer for the Narragansett Bay Fixed Station Monitoring Network ( NBFSMN ).
Monitoring New Hampshire’s Aquatic Ecosystems: Continuous Data Collection in the Lamprey River Watershed
New Hampshire’s aquatic ecosystems provide a range of ecosystem services to the state and region. Resources and services like clean water, carbon storage, climate regulation, nutrient regulation, and opportunities for recreation all depend on New Hampshire’s aquatic ecosystems remaining healthy. Jody Potter, an analytical instrumentation scientist at the University of New Hampshire (UNH), is studying these aquatic ecosystems in hopes of developing an improved understanding of ecosystem services and their interactions with climate change, climate variability, and land use changes.





















