- Home
- Solinst Water Level Temperature Sensors
Solinst Water Level Temperature Sensors
Features
- Vented or absolute pressure sensor options with 0.05% full scale accuracy
- SDI-12, RS-485 Modbus RTU, and 4-20mA protocols for interfacing with data loggers and PLC systems
- Built-in hydrophobic filters eliminate the need for desiccant replacement on vented sensors
This item is currently on order from the manufacturer, but it has not yet arrived to our warehouse.
For a current estimate of availability, please call 888-426-2151 or or fill out the form below:
This item drop ships directly from the manufacturer, and the actual lead time is dependent on availability at their warehouse.
For a current estimate of availability, please call 888-426-2151 or or fill out the form below:
Fulfillment times may be longer than usual due to component shortages and other factors outside of our control.
For a current estimate of availability, please call 888-426-2151 or or fill out the form below:
Shipping, Delivery, Order Processing & Product Availability
Fondriest uses the best carriers to make sure orders gets to you on time. Learn more about shipping times, methods, costs, and carriers.
Delivery Time
We keep you informed. Shortly after you place your order, you will receive an Order Acknowledgement email to confirm your order details, including shipping and a delivery estimate. Once your order has been prepared for shipment and ships, you will receive a Shipment Notification email with carrier and tracking information.
Shipping and Delivery Estimates
The 'Ships' timeframe is an estimate of when the item will ship from our warehouse. All items will ship at one time unless you specifically request partial shipment. In which case, the items on your order will ship as they become available. The 'Delivers' timeframe is an estimate of when the item will be delivered to your shipping address after it ships. The estimated delivery time depends on the shipping method you choose during checkout. All estimates are based on business days.
Shipping Options
Fondriest offers several convenient shipping options via UPS.
| Ground Shipping: | Products shipped via ground service are normally delivered within five business days after shipment. |
| 2-Day Shipping: | For an additional charge, Fondriest offers 2-day shipping for most products. Products shipped via two-day service prior to 4:00 p.m. EST are normally delivered by 7:00 p.m. local time two business days after shipment. |
| Overnight Delivery: | For an additional charge, Fondriest offers overnight shipping for most products. Products shipped via overnight service prior to 4:00 p.m. EST are normally delivered by 7:00 p.m. local time one business day after shipment. Earlier overnight delivery options may also be available depending on the destination. |
| Your Account: | For no additional charge, Fondriest can ship on third-party customer accounts via UPS and FedEx. Note that FedEx Ground shipments are picked up the following business day and Express shipments must be made before 1:00 p.m. EST to ensure same-day pick-up. |
Remember that these estimates are for time in transit only, and that they do not apply until the product leaves the Fondriest warehouse. As the delivery of your order is beyond Fondriest's control once your order leaves the Fondriest warehouse, we cannot assume liability for late deliveries, regardless of the delivery method you specify.
Signature Required on Most Deliveries
Most of Fondriest's shipments contain valuable equipment. If you will not be at the shipping address to accept delivery of your product, consider shipping the item to an address where someone you trust will be available to sign for your package, or accept your package if a signature is not required for the delivery. Once your order has prepared for shipment or has shipped, we are unable to change the shipping address. Title and risk of loss to all products will pass to you on delivery. If you are willing to assume the risks of delivering your order without a signature, you may authorize Fondriest to arrange for a delivery that does not require anyone to be at the delivery address.
Undeliverable Packages
Occasionally packages are returned to Fondriest as undeliverable. When the carrier returns an undeliverable package to Fondriest, please contact us to make arrangements for reshipment.
Failed Delivery Attempts
Most of Fondriest carriers make three attempts to deliver a package. After three delivery attempts, the carrier will return the package to Fondriest.
Order Processing
The estimated shipment date on your order is based on product availability, payment processing time, and warehouse processing time and does not include transit time. We do not begin payment processing until Fondriest receives all of the information that is needed and full payment or a full authorization, in the case of credit card or rental orders.
Fondriest will begin payment processing for orders placed on weekends or holidays on the next business day. Business days are Monday through Friday, excluding federal holidays.
Your order for in-stock items that are eligible for same-day shipping must be received before your local time of 2:00 p.m., pending payment processing, for there to be adequate remaining time in the day for your order to be dispatched.
Product Availability
Fondriest makes every effort to ship your product according to the estimated lead times. The estimated lead times are in business days (Monday through Friday, excluding federal holidays).
Although Fondriest makes every effort to ship your order according to the lead time provided, shipping dates may change due to changes in supply. If the lead time changes, Fondriest will contact you via email and provide a revised shipping estimate.
Fondriest makes every effort to supply the products you order, but there may be occasions when Fondriest confirms orders and later learns that it cannot supply the products, either at all or in the quantities ordered. Although rare, these occasions can include when Fondriest learns that the products no longer are being manufactured or they otherwise become unavailable, when Fondriest cannot source components for the configuration you ordered, or when there was a pricing error at the Fondriest Online Store.
In those circumstances, Fondriest will inform you and, if you are interested, Fondriest may suggest alternative products that may meet your needs. If you do not wish to order alternative products, Fondriest will cancel your order for products that cannot be supplied and for any other products that you no longer wish to order as a result, and will refund your purchase price.
We want you to be completely satisfied with your purchase. If you are not, you may initiate a return within 30 calendar days of receiving your item(s). To begin a return, you must request a Return Material Authorization (RMA) by either contacting your account representative or the general customer support address: customercare@fondriest.com. Returns without an RMA will not be accepted.
Items returned for credit must be new, unused, and in the original packaging (including any accessories, manuals, and documentation that shipped with the product). Returned items must be received by Fondriest Environmental within 14 calendar days of the issuance of the RMA. All returned items are subject to inspection and approval prior to the issuance of any credit. If the returned items have been approved, Fondriest will issue a credit based on the original method of payment. Please note that items may be subject to a manufacturer's restocking fee.
Non-Returnable Items: Fondriest does not permit the return of or offer refunds for the following products:
- Configured-to-order or customized products
- Hazardous materials
- Opened calibration reagents
- Opened software
- Software downloads
- Fondriest Gift Cards
Fondriest recommends using a carrier that offers shipment tracking for all returns. Packages should be insured for the full value in case of loss or damage. Fondriest does not assume any liability for loss or damage to the product during shipping.
- Free ground shipping
- Expedited repair and warranty service
- Lifetime technical support
- More
At Fondriest, we are committed to providing high-quality products at affordable prices with the industry's best support. Additionally, we offer:
-
Discounts
High volume purchases lead to favorable pricing, which is passed on to the customer by way of discount off MSRP.
-
Assembly, Test and Calibration
Sensors and instruments are assembled, tested and calibrated prior to shipment. A calibration report is included.
-
Lifetime Technical Support
A knowledgeable staff of applications engineers provides ongoing support for the life of the product.
-
Product Training
Applications engineers are available for webinars or personalized, on-site startup and training. Extensive measurement technology, product troubleshooting and instrument repair workshops are offered at the Field Station.
-
Extended Warranties
Warranties extended beyond factory standards are offered on many items to ensure a lasting useful life.
-
Repair
A factory-authorized service center provides fast turnaround product repair and annual maintenance.
-
Rental
Rental equipment is available to minimize downtime and cover equipment needs when projects expand.
-
Communications
Call, email or chat online with applications engineers. Email correspondence is responsive and a toll-free number is available for added convenience.
-
Quick Ship
Many orders ship on the same day and expedited shipping is available. If a product cannot be shipped immediately, customers are notified by phone or email.
-
Discounts
Overview
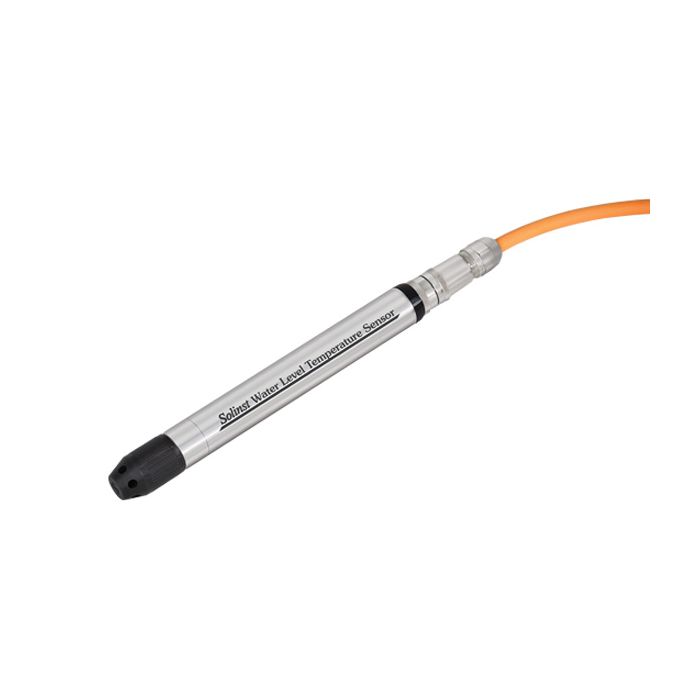
The Solinst Water Level Temperature Sensor is a compact, all-in-one submersible hydrostatic level transmitter that provides continuous, stable and accurate water level and temperature readings for a wide variety of applications. The water level pressure sensor and temperature sensor are enclosed in a slim, robust 22 mm x 192 mm (7/8" x 7.55") 316L stainless steel housing. Double O-ring seals prevent leaks, and a Faraday cage design protects against power surges and lightning.
Design
Each probe features a removable nose cone for optional use of the 1/4" NPTM threaded connection. The durable water level pressure sensor provides 0.05% FS accuracy with automatic temperature-compensated readings. There are six pressure ranges to choose from (5-200 m), with options for absolute (non-vented) and gauged (vented) pressure sensor setups.
Data Availability
The Water Level Temperature Sensor works with digital and analog protocols – MODBUS, SDI-12, and 4-20mA (add-on Current Loop Adaptor). They are easy to integrate into existing SCADA or PLC systems. Communication cable assemblies are available in lengths up to 300 meters. The cables are easily and securely attached to the sensor using a threaded connection. Simple PC software utilities are used to set up the sensor for the different protocols, perform simple diagnostics, and update sensor firmware if required. A USB-A programming cable is available for connection to the PC.
Select Options



























have been added to your cart
There are items in your cart.
Cart Subtotal: $xxx.xx
We can't add this item to your shopping cart right now. Please reload the page.
Please first select the items and quantities to add to your Cart.
In The News
Solinst Model 301 WLTS: Works Well Under Pressure
From an already successful line of water level and temperature loggers comes the new Water Level Temperature Sensor (WLTS) by Solinst, Inc. Unlike other water level measurement devices offered by Solinst, the WLTS is designed to integrate with 3rd party data loggers in industrial and environmental monitoring systems using digital communication protocols. Sensors that can be easily integrated with external devices allow for the addition of stable and continuous water level and temperature measurements to existing monitoring networks. While some water level sensors use pressure transducers to determine water level, the WLTS utilizes a hydrostatic level transmitter to record water levels and a platinum resistance temperature detector for temperature compensation.
Source Water Monitoring: How Fayette County Finds the Highest Drinking Water Quality
Safe drinking water is vital for public health infrastructure, and providing cost-effective water treatment is a top goal of drinking water utilities. To reduce these costs, counties like Fayette, Georgia, rely on source water monitoring to evaluate water quality before it reaches the treatment plant. Fayette County Water System serves about 90,000 residents and pulls water from multiple reservoirs in the area. This variety of sources offers unique benefits for the county. They have built a system that minimizes cost and maximizes choice–two water treatment plants, multiple water pumps, and multiple reservoirs. Two of the reservoirs have intake structures that allow water treatment staff to choose which level of the water column has the best quality, within 2-foot increments.
A Powerful Solution? Buoys Tracking the Potential of Ocean Alkalinity Enhancement
The climate is a complex network of interconnected systems. Halting the cascading impacts of climate change is not as straightforward as cutting anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions. Even if these emissions ceased entirely today, it would take many thousands of years for carbon dioxide (CO2) to return to pre-industrial levels. Removal of CO2 from the atmosphere is also necessary to keep global warming within the 2°C limit stipulated in the 2015 Paris Agreement . The Ocean as a Carbon Sink The ocean is the world’s largest carbon sink–it absorbs 30% of all carbon dioxide emissions and captures 90% of the excess heat generated by these emissions.


















